AnandChowdhary/drumpad
- January 26, 2018
- View on GitHub
- Processing
- 3 stars
- 3 watchers
Drumpad is an Ardunio-based music generator built for my Programming and Physical Computing project, Module 2 (Smart Environments) of Creative Technology BSc at the University of Twente.
Demo video: https://photos.app.goo.gl/tPB6ctdRPL0f0L7h2
Screenshots
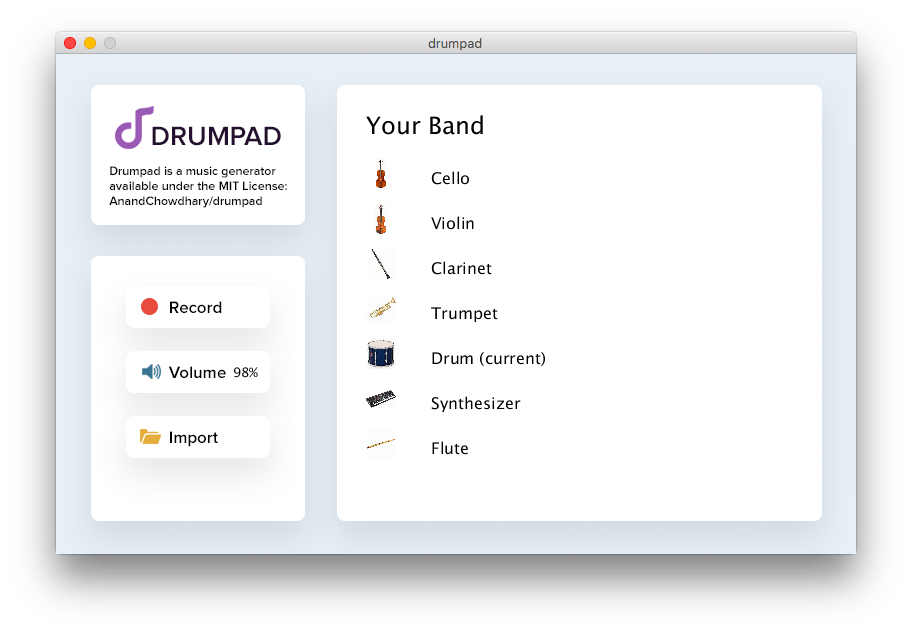
Your Band screen
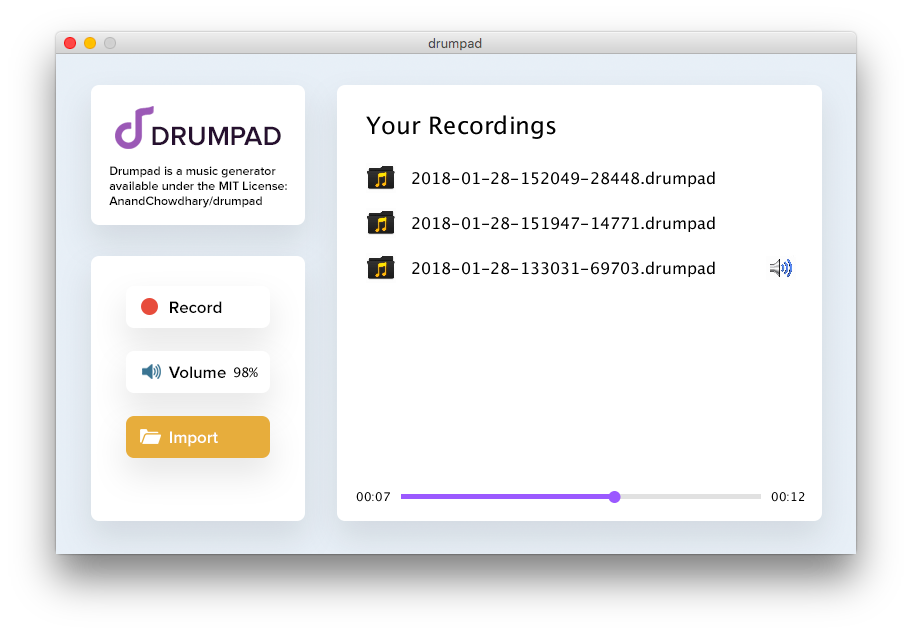
Your Recordings screen
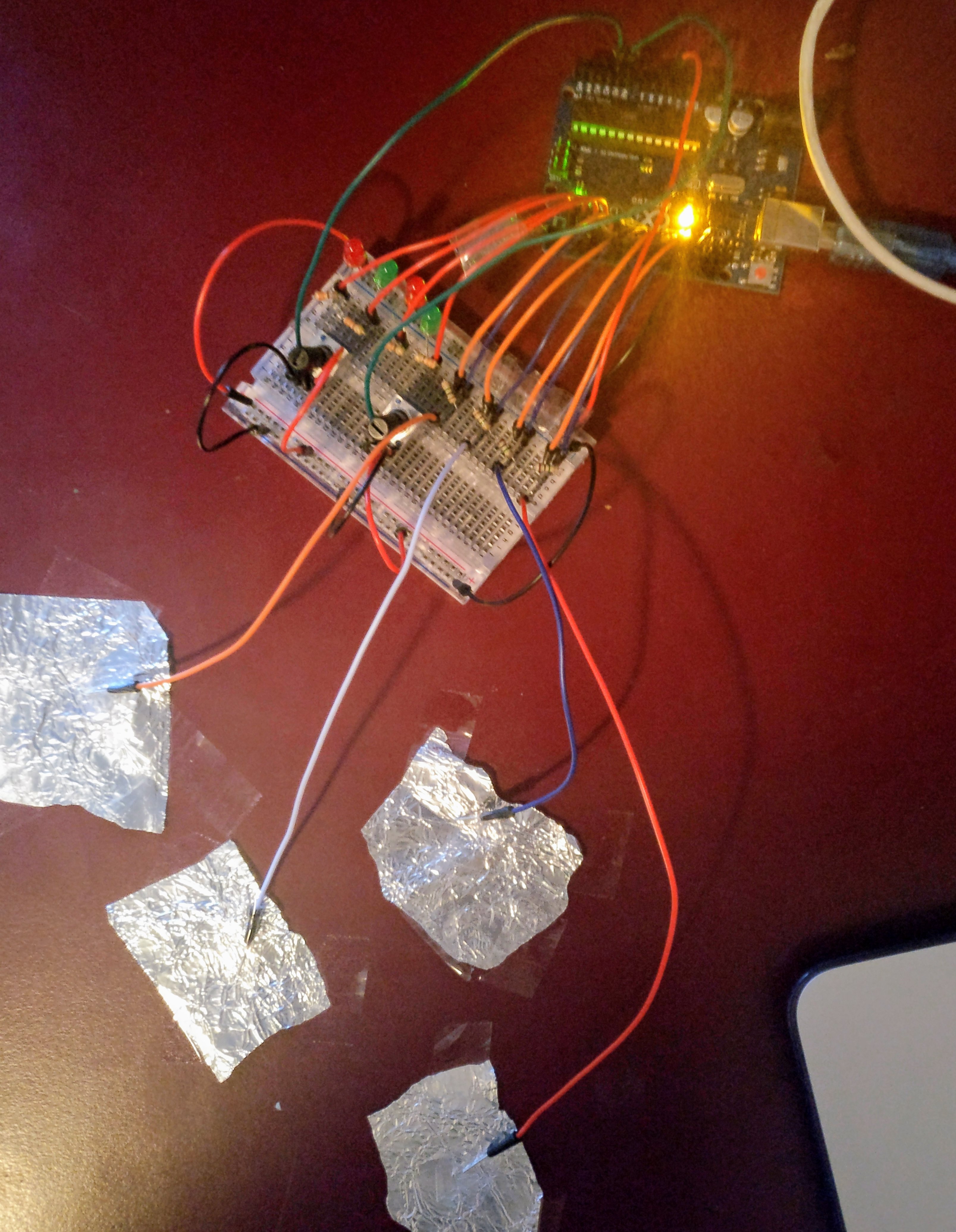
Real-life shot
Toolkit
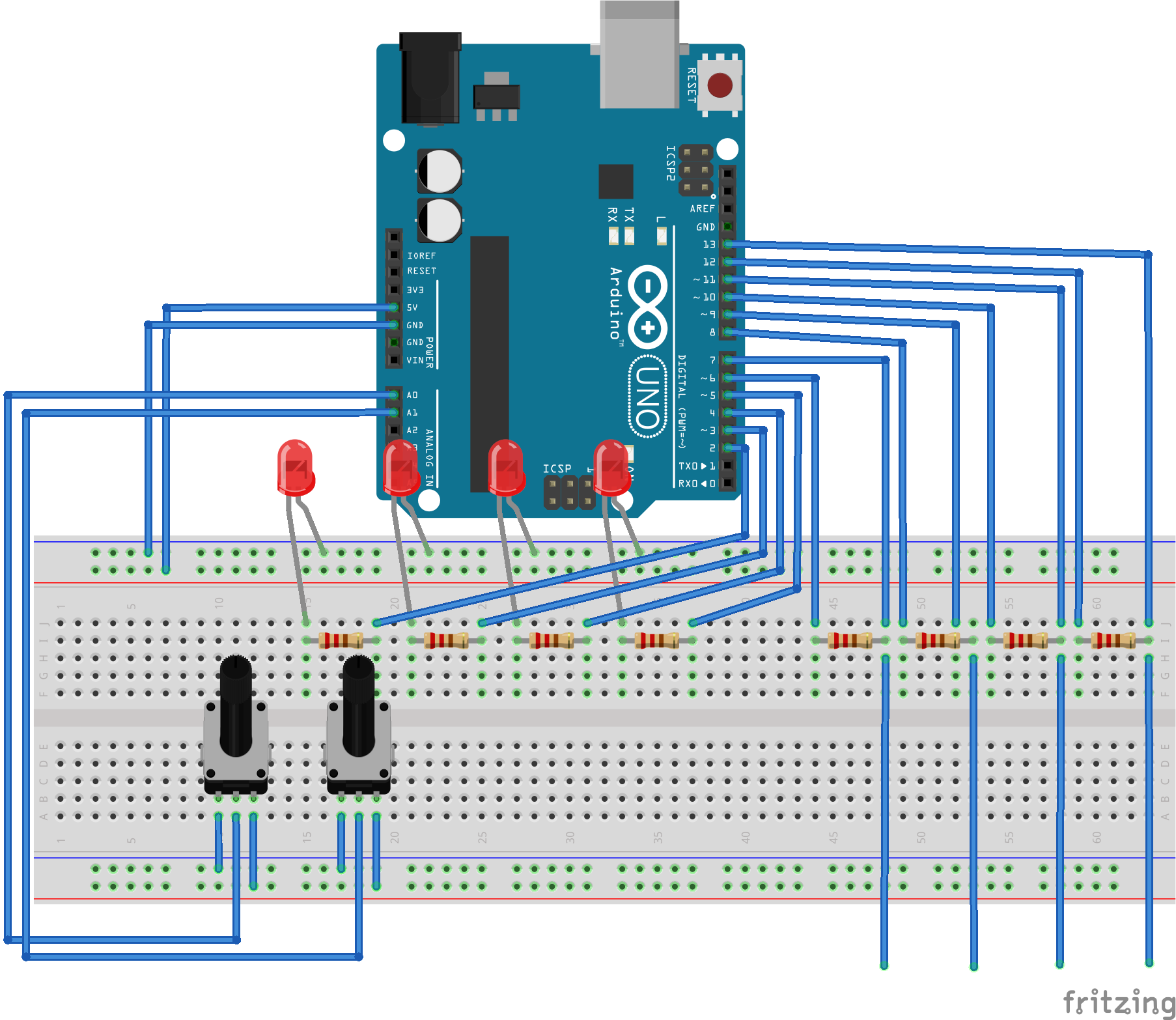
Materials
- Arduino Uno
- 4 × 1MΩ resistors for capacitive sensors
- 4 × 330Ω resistors for LEDs
- 4 × conductive input surfaces
- 4 × LEDs for output
- 2 × potentiometers
Sounds
- Kawai R50 drumkit from SampleSwap (Public Domain)
- Casio 1000P synthesizer pack by Auto-Pilot from Freesound (CC BY 3.0)
- Samples from the Music Technology Group, Department of Information and Communications Technologies, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona (CC BY 3.0)
Libraries
- CapacitiveSense.h by Paul Bagder (2009), updated by Paul Stoffregen (2010–2016) (MIT License)
- Libraries part of the Processing project (LGPL License)
- PSerial – class for serial port goodness
- Processing Sound by Wilm Thoben
How it works
Fritzing structure
Directory Structure
.
├── arduino
│ ├── CapacitiveSensor.h
│ └── drumpad.ino
└── processing
├── drumpad.pde
├── data
├── exports
└── samples
└── instrument_name
└── 0.wav … n.wav
Instruments
Drumpad automatially fetches instruments from the processing/drumpad/samples folder. Each instrument should have a corresponsing folder with WAV files from 0 to n, based on the number of input capacitive sensors. This means that it’s completely agnostic to the instruments, users have the ability to add or remove instruments from their collection.
Recording
Users can press the “Record” button to start recording their music. On completion, a data file with the extension .drumpad is created in the processing/drumpad/exports folder. When a user goes to the “Import” screen, they see a lit of their recordings, which then can be played.
License
MIT; see LICENSE.md